State Key Laboratory of Numerical Modeling for Atmospheric Sciences and
Geophysical Fluid Dynamics (LASG)
Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences

Vol. 6/No.6 July 2018
[Climate dynamics] Different pathways of the western and southern Tibetan Plateau summer snow influence on the East Asian summer climate
Highlights: The summer snow anomalies over the western and southern Tibetan Plateau influence the East Asian summer climate through distinct atmospheric pathways. The western Tibetan Plateau snow-induced anomalous atmospheric cooling affects the East Asian circulation and precipitation through a mid-latitude wave pattern. The southern Tibetan Plateau snow-induced anomalous atmospheric cooling modulates the East Asian climate variability through the North Indian Ocean convection, a west-east overturning circulation between the North Indian Ocean and the western North Pacific, and a south-north meridional teleconnection pattern along the East Asian coast.
Summary: Previous studies mostly documented the influence of cold season Tibetan Plateau snow anomalies over the South and East Asian summer climate variability. A few recent studies showed impacts of summer Tibetan Plateau snow anomalies on regional climate based on satellite retrieved snow data. Based on a whole Plateau snow cover index, Liu et al. (2014) indicated that the impacts of summer Tibetan Plateau snow cover change on circulation and precipitation over East Asia are realized through a meridional overturning circulation over the Indian sector, a tropical west-east overturning circulation over the North Indian Ocean through the western North Pacific, the tropical western North Pacific convection, and then a meridional circulation pattern along the East Asian coast. They noted that the mid-latitude Asian circulation changes were not involved in the link between the summer Tibetan Plateau snow cover and East Asian rainfall variations.
Recently, Dr. Zhibiao WANG (Ph.D. Student), Prof. Renguang WU and coauthors found that the western and southern Tibetan Plateau snow cover anomalies are nearly independent in their interannual variations. They revealed that the atmospheric circulation patterns associated with the western and southern Tibetan Plateau summer snow cover anomalies are very different. The wind anomalies in relation to the western Plateau snow anomalies are mainly confined to mid-latitude Asia, whereas those in relation to the southern Plateau snow anomalies are prominent over the tropics. They proposed that the western and southern Plateau summer snow anomalies affect the East Asian climate through different pathways. The southern Plateau snow influence follows that suggested by Liu et al. (2014) (Fig. 1b). The western Plateau snow influence is through modulating a mid-latitude Asian wave pattern (Fig. 1a). By comparing wind and precipitation anomalies when the western Plateau snow anomalies exist alone and coexist with the southern Plateau snow anomalies, they showed that the East Asian precipitation anomalies are larger when the western and southern Plateau snow anomalies coexist and work in coherence (Fig. 2).
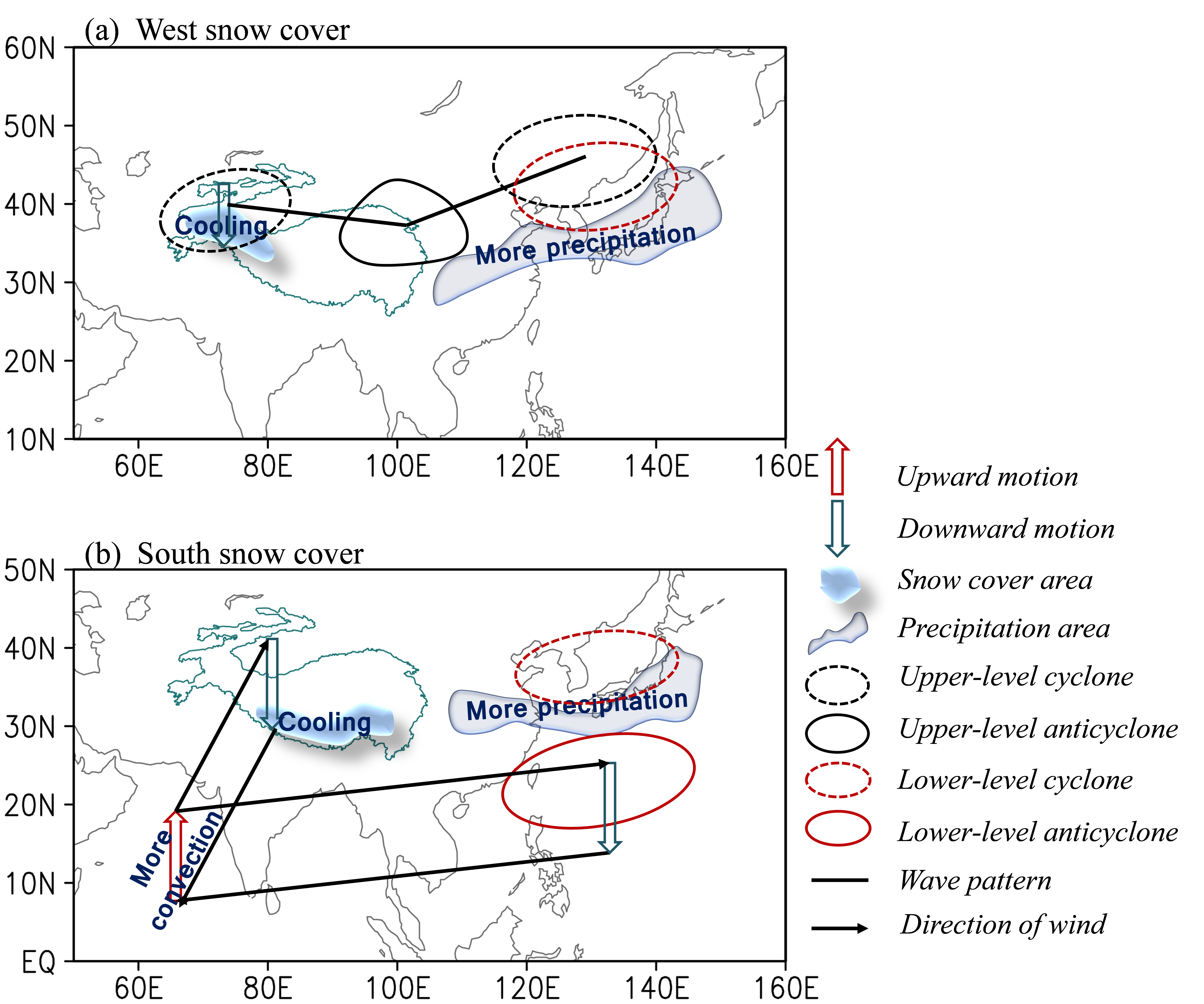
Figure 1. Schematic diagram for the influence of western (a) and eastern (b) Tibetan Plateau summer snow anomalies on the East Asian summer precipitation.
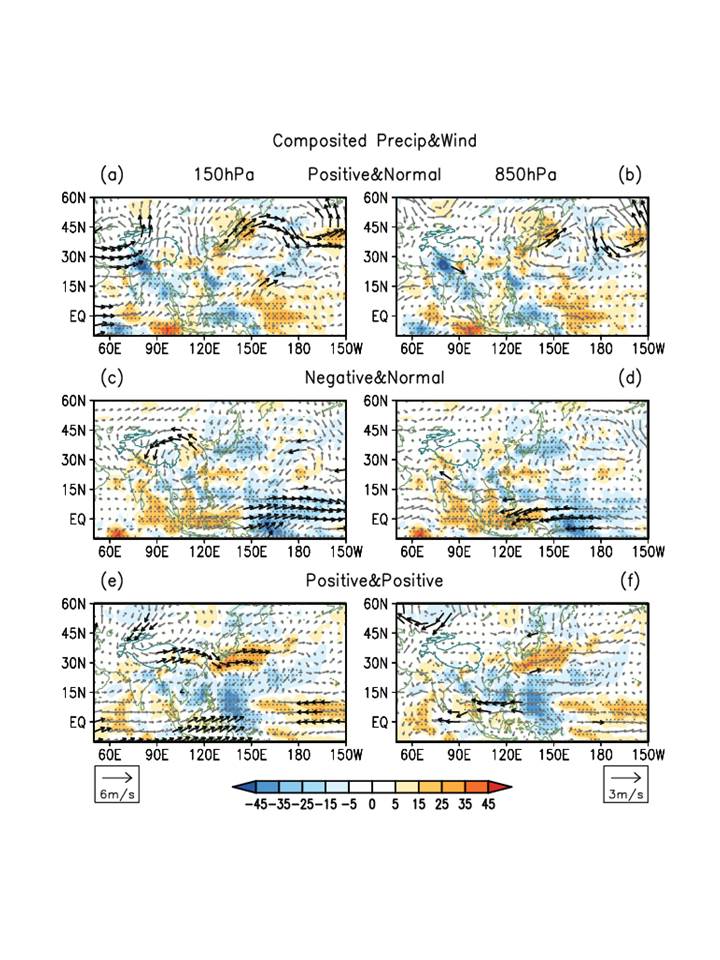
Figure 2. Composite anomalies of JJA 150-hPa winds (m/s) and precipitation (mm/month) (left), 850-hPa winds (m/s) and precipitation (mm/month) (right) in the types of years with (a, b) more snow cover in the western Plateau and normal snow cover in the southern Plateau, (c, d) less snow cover in the western Plateau and normal snow in the southern Plateau, and (e, f) more snow cover in both the western and southern Plateau. Dotted regions denote precipitation anomalies significant at the 95% confidence level and black vectors denote wind anomalies significant at the 90% confidence level. The scale for wind vectors is shown at bottom-left (a, c, e) and bottom-right (b, d, f) corner.
Citations:
Liu, G., R. Wu, Y. Zhang, and S. Nan, 2014: Summer snow cover anomaly over the Tibetan Plateau and its association with simultaneous precipitation over the Meiyu-Baiu region. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 31(4), 755-764, doi:10.1007/s00376-013-3183-z.
Wang, Z.-B., R. Wu, S.-F. Chen, G. Huang, G. Liu, and L.-H. Zhu 2018: Influence of western Tibetan Plateau summer snow cover on East Asian summer rainfall. J. Geophys. Res., 123(5), 2371-2385, doi:10.1002/2017JD028016.
Web: https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/2017JD028016
e-mail: renguang@mail.iap.ac.cn
E-mail: lasg_newsletter@lasg.iap.ac.cn
Editors: Chuanyi Wang (wangcy@lasg.iap.ac.cn), Kangjun Chen(ckj@lasg.iap.ac.cn)