State Key Laboratory of Numerical Modeling for Atmospheric Sciences and
Geophysical Fluid Dynamics (LASG)
Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences

Vol. 2/No.2 April 2017
[Model development, algorithm, and evaluation] Parallel-program Development and EvaluationofHigh-performance Advanced Regional Eta-coordinate Model (H-AREM)
Highlights:
- The new parallel programing method which building an individual supporting layer for a parallel algorithm in software by using a parallel framework is employed for regional atmospheric model.
- H-AREM significantly extends the AREM’s scalability from hundreds to thousands of cores and shortens the wall clock running time, higher resolution and refined physical processes are possible for the model due to the computational performance bottleneck has been resolved.
- Higher resolution H-AREM performance better in torrential rain simulation.
AREM is an important domestic mesoscale numerical model for predicting heavy rain,it has been used for precipitation forecasting and disastrous weather research in many institutions.When the model resolution is increased and more physical processes are included, the current AREM version cannot finish the prediction within limited time due to its low efficiency parallel computing.
To solve the problem, the model’s code is rebuilt based on the JASMIN framework, and the high-performance version of AREM is developed and named H-AREM. The combination of AREM and JASMIN framework introduces several advanced parallel algorithms to the model, including optional decomposition, dynamic load balance, and multilayer data structures, all of which benefit the computation performance. To verify the performance of H-AREM, a series of experiments is conducted, both parallel and forecast performance is involved.
The results show that H-AREM which employs 2D decomposition strategy performs better overall e.g., it is faster and more scalable thanthe version based on a message passing interface and a one-dimensional decomposition strategy.Moreover, in the H-AREM, higher resolution result in more realistic precipitation predictions. Higher resolution gets higher skill scores and lower bias in batch experiment of many rainfall cases during July to August in 2014; high resolution model simulates more realistic weather system spatial distribution and physical quantity vertical distribution in the case experiment.
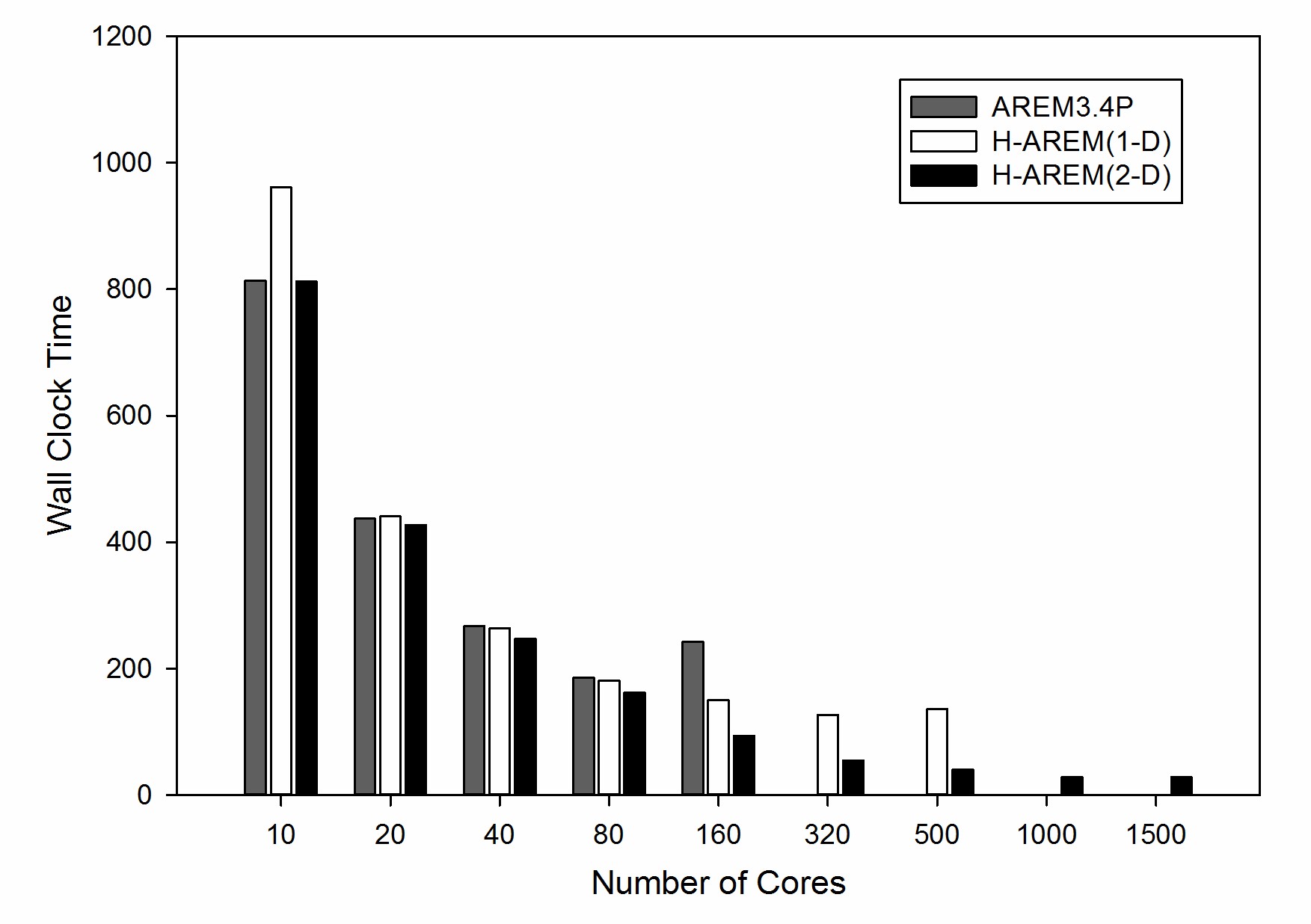
Figure 1 Model running time with different parallel strategies: AREM3.4P (dark gray), H-AREM with 1D decomposition (white), and H-AREM with 2D decomposition (black)

Figure 2 Forecast skill scores of heavy rainfall during July to August in 2014
Left: TS; Middle: TSS Right: BIAS
Red pattern: H-AREM_V3 Blue Pattern: H-AREM_V2

Figure 3 24 hours accumulated precipitation from 4 to 5July 2014: observation and forecast (mm/24h)
Initial forcast time 0000 GMT 4July 2014.
Left: observation; Middle: H-AREM_V3(8km); Right: H-AREM_V2(15km).
Rmse: root-mean-square error between observation and forcast.
Cor_index: spatial correlation index between observation and forecast.
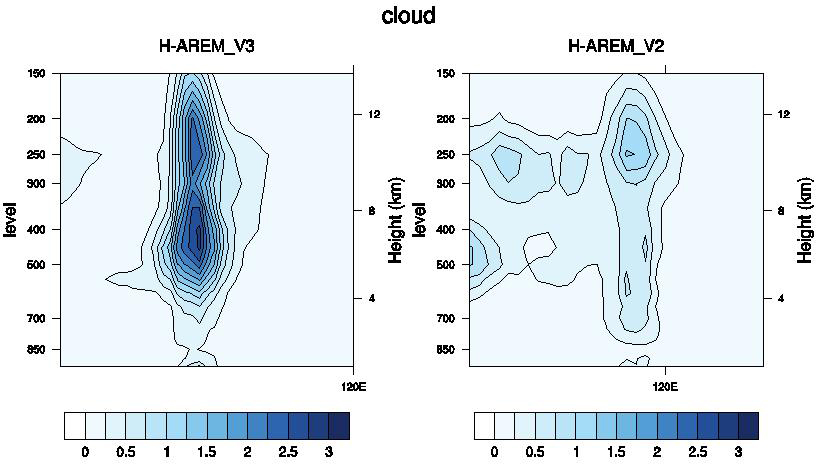
Figure 4 Vertical section of cloud water content simulation (10-3 g/g)
Initial forcast time 0000 GMT 4July 2014.
Left: H-AREM_V3(8km); Right: H-AREM_V2(15km).
Citations:
Cheng Y. F., XU Y. P., Li L. J. and Wang B. (2017) A preliminary evaluation of high-performance advanced regional eta-coordinate model(H-AREM). Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Letters, 10(1): 1-8. Doi:10.1080/16742834.2017.1248755
Download: http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/16742834.2017.1248755
XU Y. P., Cheng Y. F., Wang B.,Guo H., Pu Y. and Cheng R. (2017) Parallel-Program Development and Experiment of Regional Atmospheric Model Based on JASMIN Framework. Chinese Journal of Computational Physics, 34(1): 47-60.
Download:http://www.cjcp.org.cn/fileup/HTML/2017-1-47.htm
E-mail: lasg_newsletter@lasg.iap.ac.cn
Editors: Chuanyi Wang (wangcy@lasg.iap.ac.cn), Kangjun Chen(ckj@lasg.iap.ac.cn)