中国科学院大气物理研究所大气科学和地球流体力学数值模拟国家重点实验室
State Key Laboratory of Numerical Modeling for Atmospheric Sciences and
Geophysical Fluid Dynamics (LASG)
Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences
State Key Laboratory of Numerical Modeling for Atmospheric Sciences and
Geophysical Fluid Dynamics (LASG)
Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences

Vol.16/No.16 December 2021
Top-of-Atmosphere Radiation Budget and Cloud Radiative Effects over the Tibetan Plateau and Adjacent Monsoon Regions from CMIP6 simulations
To tackle abovementioned issues, Dr. LI Jiandong at the State Key Laboratory of Numerical Modeling for Atmospheric Sciences and Geophysical Fluid Dynamics at the Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences. and his collaborators investigates top-of-atmosphere (TOA) radiation budget (RT) and cloud radiative effects (CREs) over the TP and adjacent Asian monsoon regions including Eastern China (EC) and South Asia (SA) using the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project 6 (CMIP6) simulations. Their results show that considerable simulation biases occur but specific causes differ over these regions. Over the TP, most models underestimate the intensity of annual mean RT and cloud radiative cooling effect, and the RT during the cold-warm transition period is hard to capture due to the largest model uncertainty. The biases in surface temperature and cloud fractions substantially contribute to cloud-radiation biases over the western and eastern TP, respectively. Over EC, the intensity of RT and cloud radiative cooling effect is seriously underestimated especially in the springtime when the model spread is large, and their biases are closely related to less low-middle cloud fractions and weaker ascending motion (Figure 2). Over SA, simulation biases mainly arise from longwave radiative components associated with less high cloud fraction and weaker convection (Figure 2), with the large model spread in the summertime. The annual cycles of RT and CREs over EC and SA can be well reproduced by most models while the summertime peak of net CRE over the TP is later than the observation. The RT and its simulation bias strongly depend on the cloud radiative cooling effect over EC and SA.
This work demonstrates that contemporary climate models still have obvious difficulties in representing complex and various cloud-radiation processes in Asian monsoon regions. Particularly, model biases of the RT and CREs and their contributors in subtropical EC and tropical SA are quite different, indicating the diverse climate over Asian monsoon regions.
This work was jointly supported by the National Science Foundation of China (91737306, 91837204, 41975109, and 41730963) and published in Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres.
Reference:
Li, J. D., Z. A. Sun, Y. M. Liu, Q. L. You, G. X. Chen, and Q. Bao, 2021: Top-of-Atmosphere Radiation Budget and Cloud Radiative Effects over the Tibetan Plateau and Adjacent Monsoon Regions from CMIP6 Simulations. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 126, e2020JD034345, doi: 10.1029/2020JD034345.
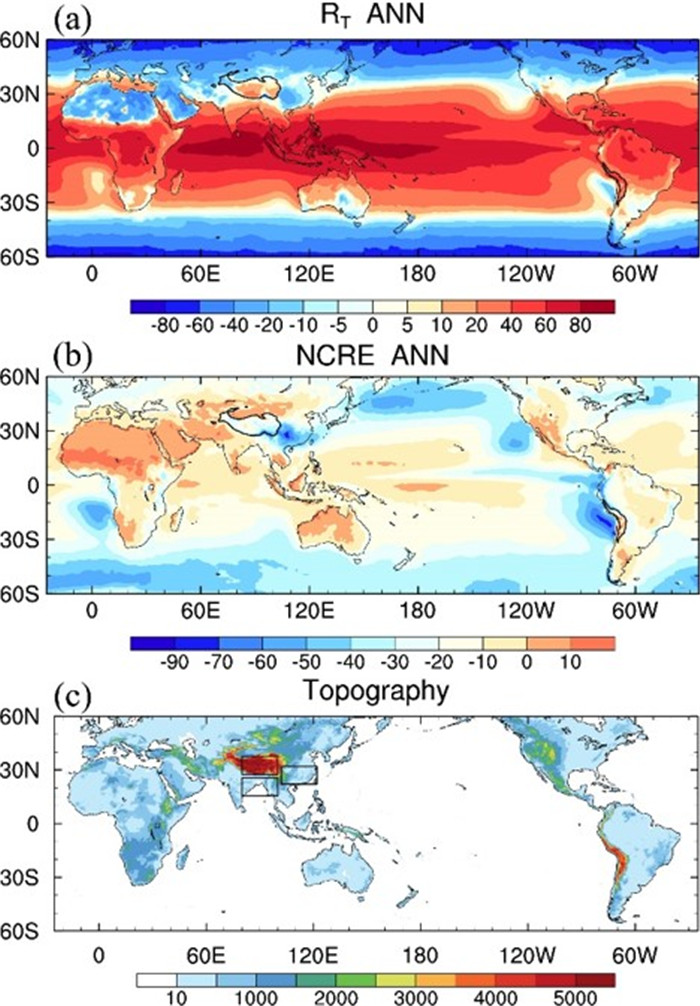
Figure 1. Distribution of annual mean (a-b) top-of-atmosphere (TOA) Radiation budget (RT; unit: W m-2) and net cloud radiative effect (NCRE; unit: W m-2) from CERES-EBAF, and (c) topography (m). In (c), three black boxes denote Eastern China (EC: 22-32° N, 102-122° E), South Asia (SA: 15.5-25.5° N, 80-100° E), and the Tibetan Plateau (TP: 27.5-37.5° N, 80-100° E), respectively.
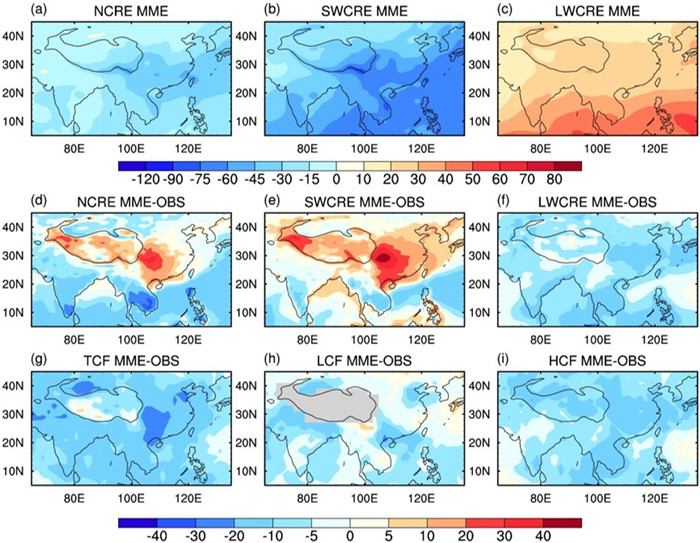
Figure 2. Distribution of annual mean (a-c) net, shortwave, and longwave CREs (NCRE, SWCRE, and LWCRE) (W m−2) in CMIP6 AMIP MME with satellite simulator output, and differences in (d-f) NCRE, SWCRE, LWCRE (W m−2), (g-i) total, low, and high cloud fraction (TCF, LCF, and HCF) (%) between CMIP6 AMIP MME with satellite simulator output and GOCCP during 2007-2014.
Link: https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1029/2020JD034345
Contact: LI Jiandong, lijd@mail.iap.ac.cn
Add: No.40, Huayanli, Beichen West Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing P.O. Box 9804, 100029, China
E-mail: lasg_newsletter@lasg.iap.ac.cn
Editors: Chuanyi Wang (wangcy@lasg.iap.ac.cn), Kangjun Chen(ckj@lasg.iap.ac.cn)
E-mail: lasg_newsletter@lasg.iap.ac.cn
Editors: Chuanyi Wang (wangcy@lasg.iap.ac.cn), Kangjun Chen(ckj@lasg.iap.ac.cn)