中国科学院大气物理研究所大气科学和地球流体力学数值模拟国家重点实验室
State Key Laboratory of Numerical Modeling for Atmospheric Sciences and
Geophysical Fluid Dynamics (LASG)
Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences
State Key Laboratory of Numerical Modeling for Atmospheric Sciences and
Geophysical Fluid Dynamics (LASG)
Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences

Vol.14/No.14 Ddcember 2020
Scientists Look into the Tropopause to Find the Early Signals of Persistent Strong Rainfall
To find the signal, Prof. XIAO Ziniu and his team with the State Key Laboratory of Numerical Modeling for Atmospheric Sciences and Geophysical Fluid Dynamics (LASG), Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, in collaboration with Civil Aviation University of China, Guangdong Climate Center and other institutes in China, used a powerful analysis tool --the intraseasonal oscillation (ISO) of isentropic potential vorticity (PV)--to track precursors near the tropopause preceding persistent strong precipitation in South China. The results were published on Sep. 2 in Climate Dynamics.
"The early signals leading to persistent heavy rainfall in South China originate from two regions: the Arctic region and the tropical monsoon region. 20 days before the peak rainfall, the western Tibetan Plateau and the northern side of the East Asian westerly jet near the tropopause are two transit points for the anomalous potential vorticity to strengthen and change propagating direction." said ZHAO Liang, the first author of the study. ZHAO is a Senior Engineer with LASG.
It is very critical for prediction to find the special early configuration of synoptic systems for the occurrence of persistent heavy rainfall events. "We find that when the anomaly low pressure is surrounded by three anomaly high pressure systems, including South Asia high, Okhotsk Sea blocking high and the western Pacific subtropical high, this special situation is often responsible for the following persistent heavy rainfall in South China." said XIAO.
According to this study, 10 days before the peak rainfall, the joint action of the South Asia high and the Okhotsk Sea blocking high compresses the anomaly cold air between them two highs, and forms a narrow and steady cold air transport channel on the inclined isentropic surface. It enables the cold air to a lower latitude and continually meet with the warm and moist air in South China brought by the anomaly strong subtropical high, forming a persistent heavy precipitation.
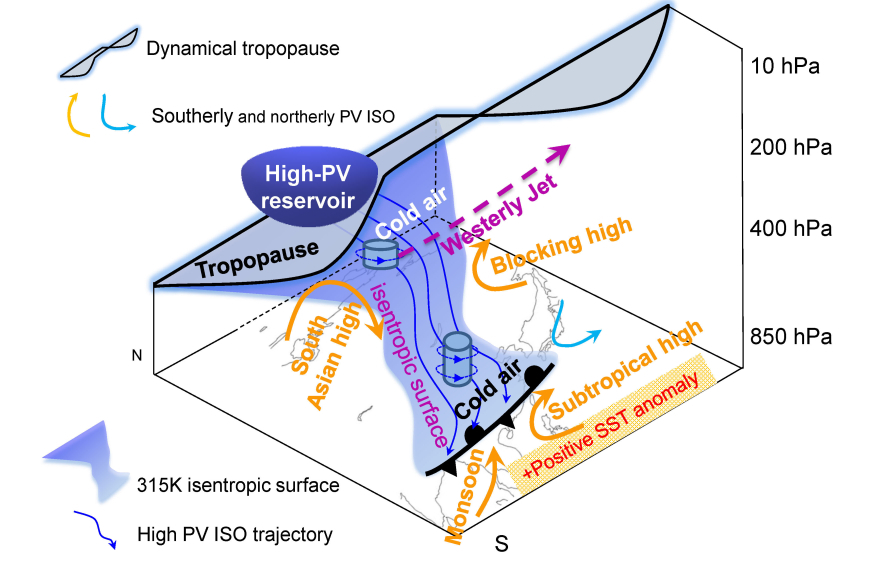
Schematic illustration of precursor signal and synoptic system configuration along isentropic surface for persistent strong precipitation events in South China. (Image by ZHAO Liang)
"Our finding provides a new potential factor for the prediction of regional persistent heavy rainfall," said XIAO.
This research was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China and the Strategic Priority Research Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Reference:
Liang Zhao, Haiwen Liu, Yamin Hu, Huhua Cheng, Ziniu Xiao. Extratropical extended-range precursors near the tropopause preceding persistent strong precipitation in South China: a climatology. Climate Dynamics, 2020, DOI: 10.1007/s00382-020-05437-6. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00382-020-05437-6
Link: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00382-020-05437-6
Contact: ZHAO Liang, zhaol@lasg.iap.ac.cn
XIAO Ziniu, xiaozn@lasg.iap.ac.cn
Add: No.40, Huayanli, Beichen West Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing P.O. Box 9804, 100029, China
E-mail: lasg_newsletter@lasg.iap.ac.cn
Editors: Chuanyi Wang (wangcy@lasg.iap.ac.cn), Kangjun Chen(ckj@lasg.iap.ac.cn)
E-mail: lasg_newsletter@lasg.iap.ac.cn
Editors: Chuanyi Wang (wangcy@lasg.iap.ac.cn), Kangjun Chen(ckj@lasg.iap.ac.cn)